Sahara Dust Storm: Nature’s Powerful Transcontinental Journey
A deep dive into Sahara dust storms, their origins, global impacts, health risks, and environmental significance. Discover how this dusty phenomenon shapes our world.
What is a Sahara Dust Storm?
When you hear the phrase “Sahara dust storm,” it might conjure images of swirling sands in the vast desert. While you’re not entirely wrong, there’s so much more to it. Sahara dust storms are vast plumes of fine, dry particles from the Sahara Desert that get lifted into the atmosphere and travel across continents, sometimes reaching as far as the Americas and Europe. It’s not just dust; it’s a phenomenon that affects air quality, weather patterns, and even marine life.
This dust is incredibly fine, almost like talcum powder, and is carried by strong winds from the desert floor into the upper atmosphere. From there, it can be transported thousands of miles, often crossing the Atlantic Ocean. It’s mind-blowing to think that a particle of dust from Africa can end up on a car windshield in Texas or fertilize the Amazon Rainforest. These storms aren’t just local events – they are global players in atmospheric dynamics.
The Origins of Sahara Dust Storms
Sahara dust storms originate from the world’s largest hot desert, the Sahara. Covering roughly 3.6 million square miles, this desert is not just a sea of sand dunes. It’s a complex ecosystem with varied terrain, and it’s from its arid surface that millions of tons of dust are swept up annually.
Strong surface winds, especially from the northeast trade winds, kick up loose dust and sand. These winds are particularly active during the late spring to early autumn months. The dust gets lofted into the Saharan Air Layer (SAL), a dry, hot air mass that forms over the desert. Once it hits the upper atmosphere, it can travel with prevailing winds across continents and oceans.
Global Impact of Sahara Dust Storms
You might be wondering: why does it matter if some dust blows around? Turns out, it matters a lot. Sahara dust storms play a huge role in Earth’s climate system. One of the most surprising facts is their ability to fertilize rainforests. The Amazon Basin, for instance, receives essential phosphorus nutrients carried by Sahara dust. Without this dusty delivery system, the Amazon might not be as lush as it is.
In addition to fertilization, Sahara dust storms can also suppress hurricanes. The dry, dusty air of the SAL can inhibit the formation of tropical storms in the Atlantic. While it may sound counterintuitive, this natural atmospheric shield can be a blessing during hurricane season.
Health Effects of Sahara Dust Storms
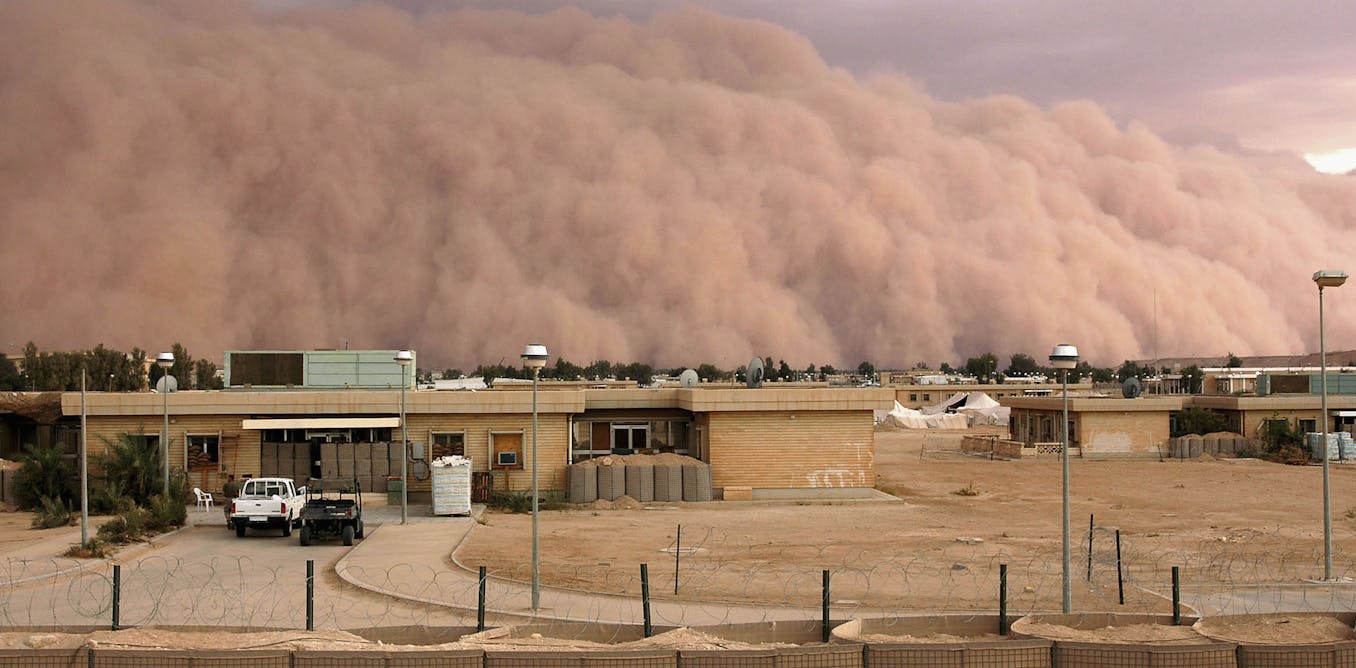

Now, let’s talk health. Breathing in fine dust particles from a Sahara dust storm isn’t exactly a spa treatment. These storms can significantly affect air quality, especially in areas far from the desert itself. When the dust settles in populated areas, it can irritate the respiratory system and trigger allergies or asthma.
Children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing respiratory conditions are especially vulnerable. Authorities often issue health advisories when high concentrations of dust are detected in the atmosphere. In severe cases, prolonged exposure to these particles can lead to chronic respiratory issues.
Environmental Impact of Sahara Dust Storms
Beyond human health, these dust storms have a profound environmental impact. Besides fertilizing rainforests, Sahara dust also affects ocean ecosystems. The iron content in the dust can stimulate the growth of phytoplankton, which are crucial for the marine food chain and carbon cycle.
But not all impacts are beneficial. When dust blankets regions with snow or ice, it darkens the surface, causing faster melting due to increased heat absorption. This can accelerate glacial retreat and contribute to sea-level rise. In short, the environmental effects are a mixed bag – some good, some concerning.
Sahara Dust Storms and Weather Patterns
These dust storms are more than just dry winds; they actively shape weather. When large dust plumes move into the atmosphere, they can affect cloud formation and precipitation patterns. In some areas, the dust can lead to drier weather by absorbing sunlight and stabilizing the atmosphere, which suppresses cloud formation.
On the flip side, in certain regions, the dust can act as cloud condensation nuclei, aiding in cloud formation and even precipitation. It’s a complex dance of atmospheric chemistry and physics, but one thing is clear: Sahara dust storms are not passive events – they interact with the atmosphere in dynamic ways.
Seasonal Patterns of Sahara Dust Storms
These storms are not random. There’s a rhythm to their appearance, largely dictated by seasonal wind patterns and weather systems. The most active period for Sahara dust transport tends to be between late spring and early autumn, peaking during the summer months.
During this time, the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) shifts northward, and the Saharan Air Layer becomes more prominent. Meteorologists track these storms using satellite imagery, and forecasts often include advisories for dust movement, especially during the high season.
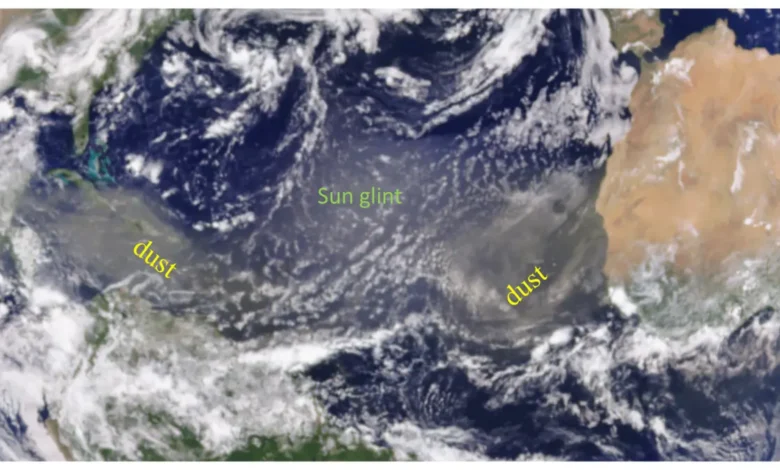
Tracking and Monitoring Sahara Dust Storms
Thanks to modern technology, we can now monitor these dust storms with impressive accuracy. Satellite imagery plays a big role in tracking the movement of dust plumes from Africa to the Americas. NASA, NOAA, and other agencies regularly release visual maps showing the density and reach of the dust.
Ground-based air quality sensors also help detect the presence of fine particulate matter. Combining satellite data with ground observations allows for more accurate forecasts and health advisories. This level of monitoring is essential for preparing populations and mitigating the impact of these massive storms.
Economic and Social Impacts
Believe it or not, Sahara dust storms also have economic implications. In areas where visibility drops drastically due to airborne dust, transportation can be disrupted. Flights might get delayed or canceled, and road travel can become hazardous.
Additionally, the fine dust can damage machinery and infrastructure. In agriculture, while some soils might benefit from nutrient-rich dust, crops and livestock can suffer from reduced air quality and sunlight. There’s also a social aspect: people may have to stay indoors, events might be postponed, and health services could face increased demand.
How to Protect Yourself During a Dust Storm
If you’re living in or traveling to an area affected by Sahara dust storms, there are steps you can take to stay safe. First and foremost, stay informed. Pay attention to air quality indices and follow public health advisories.
Wearing masks, particularly those rated for particulate filtration, can help reduce inhalation of harmful particles. Keeping windows and doors closed, using air purifiers indoors, and avoiding outdoor activities during high-dust periods are all practical ways to minimize exposure.
Myths and Misconceptions About Sahara Dust Storms
There’s no shortage of myths surrounding these storms. One common belief is that they only affect Africa. As we’ve seen, that’s far from the truth. These storms can travel across oceans and affect continents thousands of miles away.
Another misconception is that they’re always dangerous. While they do pose health and environmental risks, they also provide crucial nutrients to ecosystems and help regulate global weather. Like many natural phenomena, Sahara dust storms are complex and multifaceted.
Sahara Dust Storms and Climate Change

Climate change is altering many natural processes, and Sahara dust storms are no exception. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can influence the frequency and intensity of these storms. Some studies suggest that a warming climate could either increase or decrease dust emissions, depending on regional factors.
What’s clear is that monitoring these trends is vital. Understanding how Sahara dust interacts with the climate system helps us predict future impacts and develop strategies for adaptation. It’s another piece of the ever-complicated climate puzzle.
Sahara Dust Storms in Popular Culture
From movies to news headlines, Sahara dust storms have captured the public imagination. They’re often portrayed as dramatic, mysterious forces of nature. While Hollywood might exaggerate their impact for cinematic effect, the reality is no less fascinating.
In literature and folklore, dust storms are sometimes seen as omens or symbols of change. This cultural perspective underscores how deeply these natural events are woven into human experience, particularly in regions close to the Sahara.
“From the dunes of the Sahara to the shores of the Americas, each grain of dust carries a story of connection and change.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Sahara dust storm? A Sahara dust storm is a massive movement of fine dust particles from the Sahara Desert into the atmosphere, often traveling across continents and oceans.
How far can Sahara dust travel? These dust particles can travel thousands of miles, often reaching North and South America, Europe, and even as far as the Caribbean.
Are Sahara dust storms dangerous to health? Yes, they can affect air quality and pose risks, especially for individuals with respiratory issues. It’s important to follow health advisories during high-dust periods.
Do Sahara dust storms affect the weather? Absolutely. They can influence cloud formation, rainfall patterns, and even suppress hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean.
Can Sahara dust storms be seen from space? Yes. Satellite imagery often captures large dust plumes moving from the African continent across the Atlantic, making them visible from space.
Why do Sahara dust storms happen? They occur due to strong surface winds that lift fine dust into the atmosphere, particularly during certain seasons when atmospheric conditions are favorable.
Are Sahara dust storms increasing due to climate change? Climate change may affect the frequency and intensity of these storms, but ongoing research is needed to understand the full impact.
How can I protect myself from Sahara dust? Stay indoors during high dust periods, use air purifiers, wear masks, and monitor local air quality reports.
Final Thoughts
Sahara dust storms are one of the Earth’s most incredible natural phenomena. From fertilizing rainforests and regulating hurricanes to posing health risks and altering weather, these dusty travelers play a far greater role than most of us realize. With climate change and improved technology, our understanding of these storms continues to evolve. Staying informed and prepared is key to living with this awe-inspiring force of nature.

